KAIST develops core technology for world's first surface plasmon OLED
성수 최 2009-07-22 View. 5,762Prof. Choi Kyung-chol team's technology to allow for low-cost, normal temperature OLED processing.
The Korea Advanced Institute of Technology (President Suh Nam-pyo) said on July 9 that a research team led by Prof. Choi Kyung-chol at the institute's electrical and electronic engineering department had become the first in the world to develop a core technology that significantly enhances the efficiency of OLEDs, an electronic display device.
Prof. Choi's team discovered that when a material inducing surface plasmon is combined with light generated from an OLED using nano-size silver (Ag) particles, the speed at which light emission recombines increases, thus significantly enhancing the brightness of the OLED.
Additionally, the team increased the efficiency of light emission by up to 75 percent by allowing for low-cost, normal temperature OLED processing using surface plasmons through the application of an evaporation method for the first time in the world.
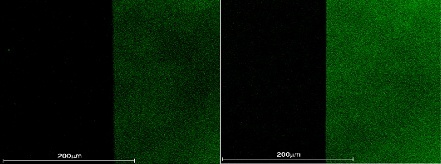
(Photo) A photo of OLED light emission using surface plasmons compared with a photo of that light emission in a conventionally structured OLED.
The study is drawing keen attention for inventing a new display device that combines OLED, a next-generation display technology, with surface plasmon technology using low-cost nanoparticles.
Prof. Choi said, "The technology that has been developed using surface plasmons is a new technology that can enhance the emission efficiency of OLEDs," adding, "The technology is expected to make important contributions to the acquisition of core technology and to the development of OLED and flexible display technology."
The study was published in Applied Physics Letters, a world-renowned journal in the applied physics field, and Optics Express, the most prestigious journal in the optics field. The study was conducted with support from the "Frontier research center program" of the Korea Research Foundation (Chairman Park Chan-mo), and from the "KAIST high risk, high return program" at the Nanopap Center (President Lee Hee-chul).
Yoo Sang-young,
young at hellodd.com
[July 21, 2009]
- - - - - - -
Source - HelloDD.com

 Delete Article!
Delete Article!